Software Development Cost Explained: What You Really Pay For
Understanding software development cost is one of the biggest challenges for founders, product managers, and decision-makers. Many projects start with optimistic budgets, only to exceed expectations once real development begins.
This article explains what software development cost actually includes, what drives it up or down, and how to estimate it realistically before committing time and money.
What Is Software Development Cost?
Software development cost is the total investment required to plan, design, build, test, launch, and maintain a software product.
It is not just "developer hours." A realistic cost includes:
- Team labor (multiple roles, not just developers)
- Design and user experience
- Feature implementation
- Testing and quality assurance
- Infrastructure and third-party services
- Documentation, support, and buffers
Projects that ignore any of these elements almost always exceed budget later.
The Biggest Cost Drivers in Software Development
1. Team Composition and Experience
People are the primary cost factor in any software project.
Typical roles include:
- Frontend developer
- Backend developer
- UI/UX designer
- QA engineer
- Project or product manager
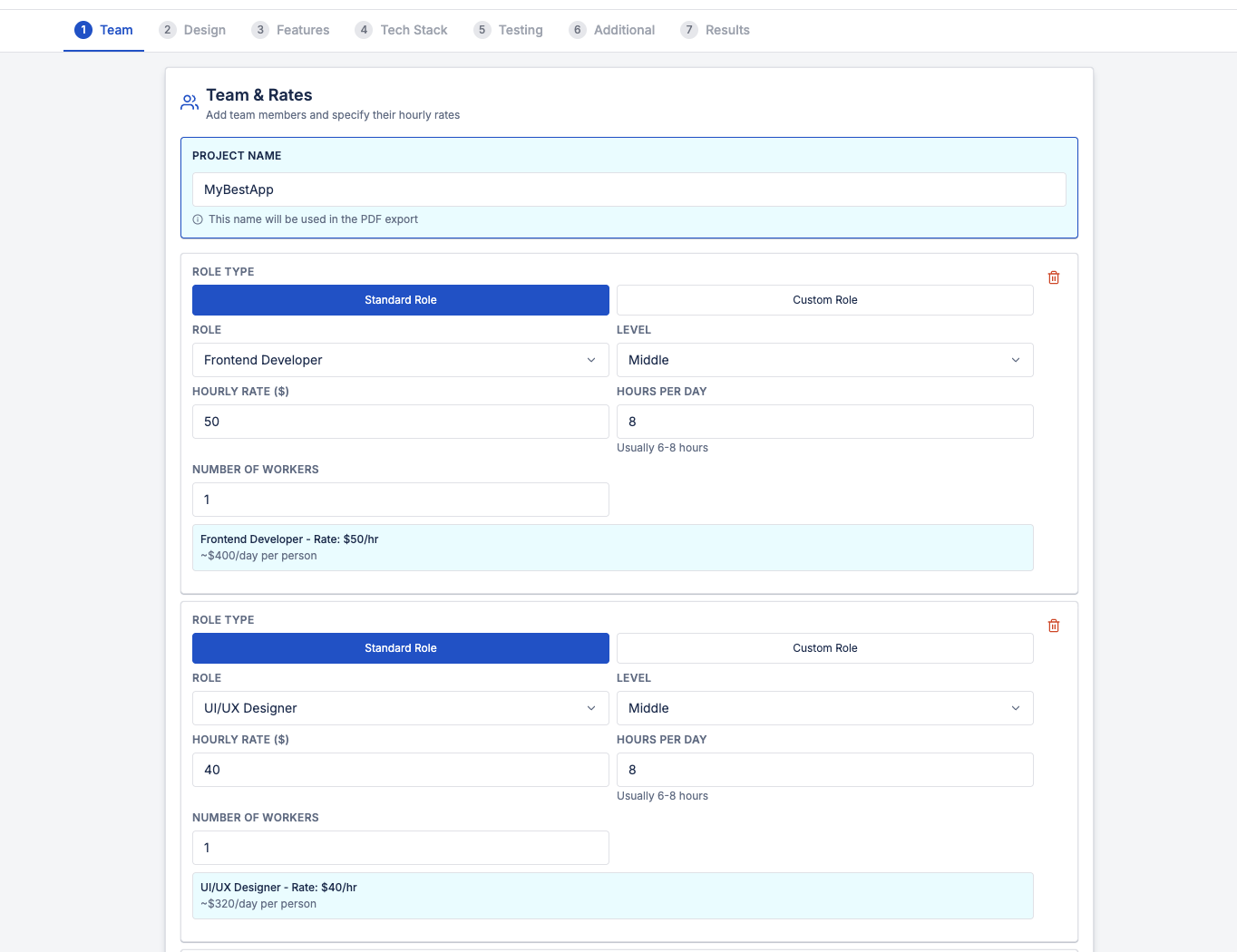
Each role has:
- A different hourly rate
- Different time involvement
- Different impact on quality and speed
A senior engineer may cost more per hour but reduce total cost by avoiding rework and technical debt.
2. Design Scope and Complexity
Design cost depends on much more than visuals.
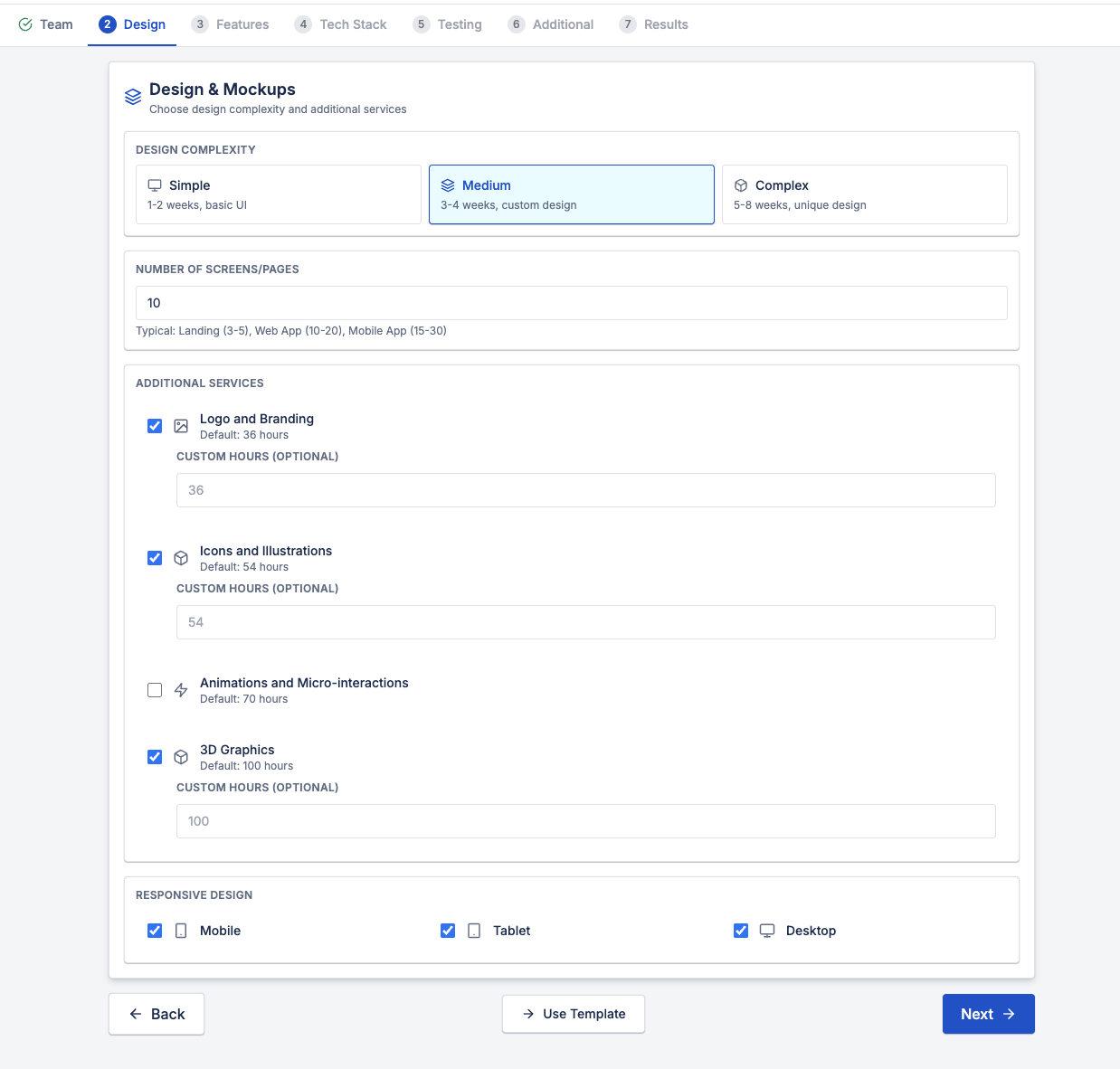
Key factors include:
- Number of screens or pages
- Interaction complexity
- Custom components vs reusable patterns
- Responsive design for mobile, tablet, and desktop
- Branding, icons, animations, and illustrations
For example, a web app with 10–20 screens and medium complexity can require weeks of design work, not days.
3. Features and Functional Requirements
Features are where software development cost grows fastest.
Examples of high-impact features:
- Authentication and security (login, OAuth, 2FA)
- Payments and subscriptions
- Real-time communication
- Data search and filtering
- Analytics dashboards
- Admin panels and user management
Each feature includes:
- Frontend logic
- Backend logic
- Validation and edge cases
- Testing effort
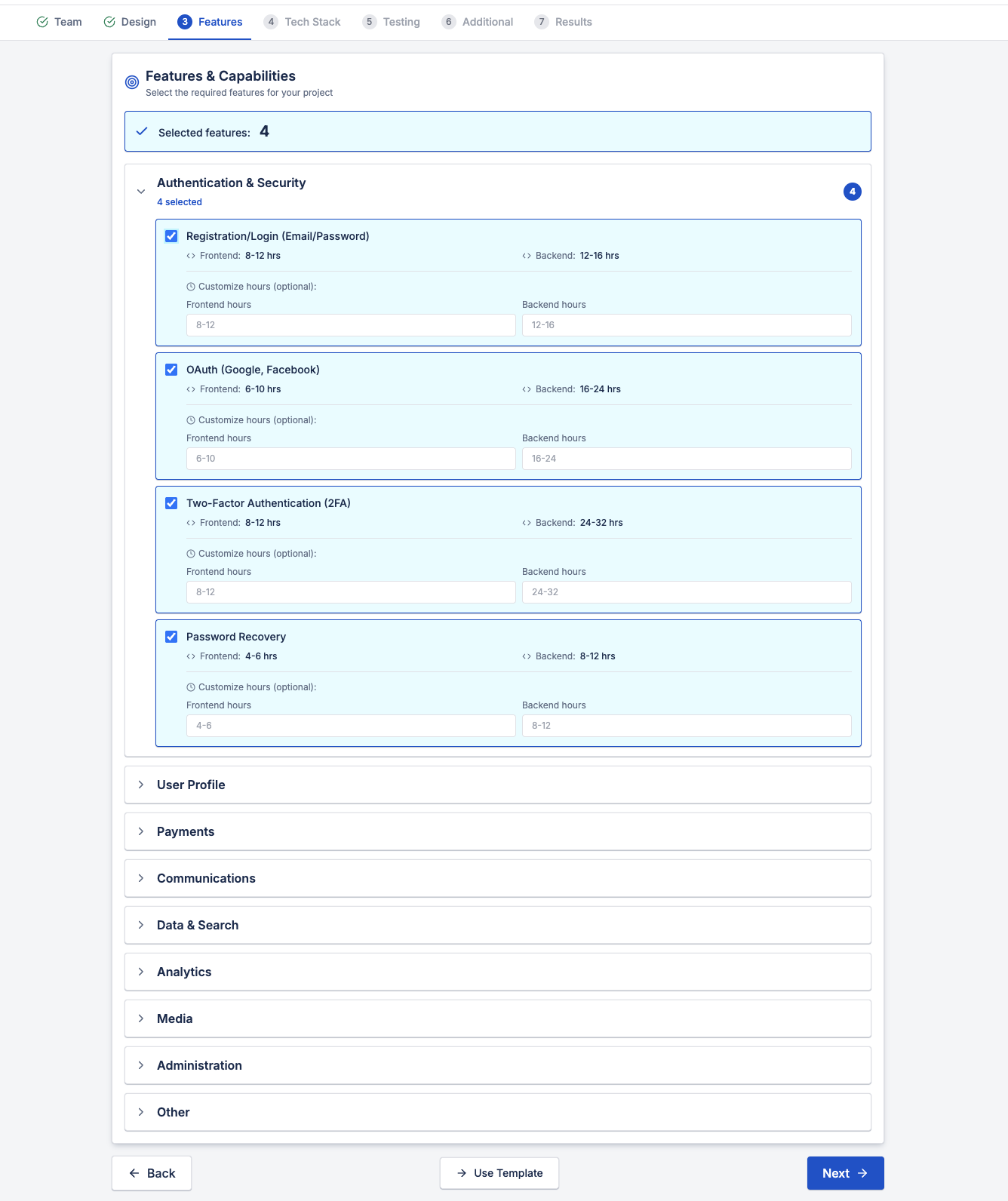
Counting features without estimating effort leads to false budgets.
4. Technology Stack Choices
Your technology stack influences:
- Development speed
- Maintenance cost
- Scalability
- Hosting expenses
Different stacks suit different goals:
- JavaScript-based stacks for MVPs and SaaS
- Enterprise stacks for long-term, complex systems
- Serverless architectures for quick launches
- High-performance stacks for real-time applications
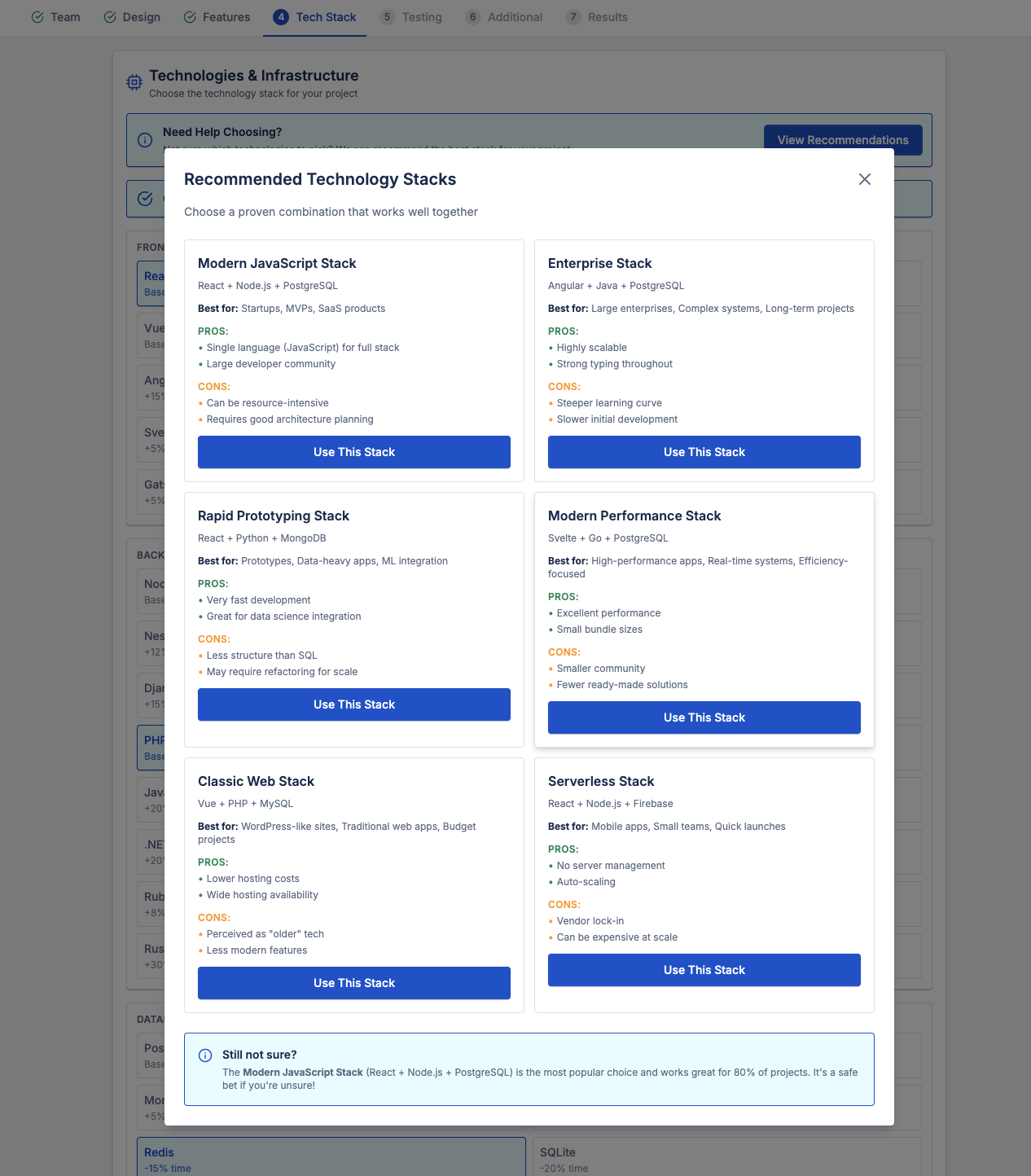
Technology decisions should balance cost today with cost of change tomorrow.
5. Testing and Quality Assurance
Testing is often underestimated or skipped — and later paid for with bugs and delays.
Professional software development cost includes:
- Manual testing
- Automated tests (unit, integration, E2E)
- Regression testing
- Performance and security checks
Industry standards allocate 15–25% of development time to QA. Skipping this phase increases long-term cost dramatically.
6. Additional and Ongoing Costs
Many budgets fail because they ignore what happens after launch.
Common additional costs include:
- Post-launch support and maintenance
- Bug fixes and updates
- Technical documentation
- User guides
- Domain and SSL certificates
- API usage and third-party services
- Software licenses and tools
A realistic budget includes a buffer (15–25%) for unexpected changes.
Why Software Development Cost Varies So Widely
You may see estimates ranging from a few thousand to hundreds of thousands of dollars for "the same app."
That's because cost depends on:
- Scope definition
- Feature depth
- Team location and rates
- Quality expectations
- Long-term scalability requirements
Two projects with similar ideas can have completely different costs based on execution choices.
Fixed Price vs Time & Materials
Understanding pricing models helps interpret estimates.
Fixed price:
- Predictable upfront cost
- Limited flexibility
- Higher risk premium
Time & materials:
- Transparent cost structure
- Flexible scope
- Better for evolving products
Most modern software projects benefit from time-based estimates presented as ranges.
Why Estimation Ranges Are More Honest Than Fixed Numbers
Software development involves uncertainty:
- Requirements evolve
- Integrations introduce risk
- User feedback changes priorities
Single-number estimates create false confidence. Ranges allow better planning and decision-making.
Professional teams plan with confidence intervals, not promises.
How to Estimate Software Development Cost Before Hiring a Team
Before engaging agencies or developers, you should:
- Define core features
- Decide target platforms (web, mobile)
- Choose approximate design complexity
- Define team roles and rates
- Include testing and buffers
Modern estimation tools structure this process and make assumptions visible instead of hidden.
How Projecto Helps Estimate Software Development Cost
Projecto applies industry-standard estimation logic by:
- Breaking projects into roles, features, and stages
- Assigning realistic effort ranges
- Converting effort into cost using real rates
- Including testing, support, and buffers
The result is a transparent, adjustable cost range, not a guess.
Final Thoughts
Software development cost is not just about code. It reflects decisions about quality, scope, risk, and long-term sustainability.
Understanding what you're really paying for allows you to:
- Avoid budget surprises
- Make informed trade-offs
- Build better products with fewer regrets
FAQ
What is software development cost?
Software development cost is the total investment required to plan, design, build, test, launch, and maintain a software product. It includes team labor, design, feature development, testing, infrastructure, and ongoing support.
What factors affect software development cost the most?
The biggest cost drivers are team composition and experience, design complexity, number and complexity of features, technology stack choices, testing requirements, and post-launch support.
Why does software development cost vary so much?
Software development cost varies due to differences in project scope, feature depth, quality expectations, team rates, technology decisions, and long-term scalability requirements.
Does software development cost include testing?
Yes. A realistic software development cost includes both manual and automated testing. Industry best practices typically allocate around 15–25% of total development time to quality assurance.
Can software development cost be estimated before development starts?
Yes. High-level software development cost can be estimated early using assumptions about scope, features, team roles, and design complexity. Accuracy improves as requirements become clearer.
Does software development cost include maintenance?
It should. Maintenance, updates, bug fixes, and ongoing support are recurring costs that should be considered part of the total software development cost.