How to Calculate Project Cost: A Complete Guide
Estimating the cost of a software project is one of the most challenging — and most critical — steps in product planning. Inaccurate project cost calculation often leads to budget overruns, missed deadlines, and strained relationships between founders, teams, and stakeholders.
This guide explains how to calculate project cost realistically, what factors truly influence software development cost, and how modern estimation tools help teams plan with confidence.
What Is Project Cost Calculation?
Project cost calculation is the process of estimating the total financial investment required to design, build, test, and deliver a software product.
A realistic calculation goes far beyond a single number. It considers:
- Team composition and hourly rates
- Design scope and complexity
- Feature set and technical requirements
- Quality assurance and testing effort
- Additional costs such as documentation, support, and buffers
The goal is not perfection, but a reliable planning range that supports informed decisions.
Why Most Software Projects Go Over Budget
Many projects exceed their initial budget because estimates are based on assumptions rather than structured analysis.
Common reasons include:
- Features defined too vaguely
- Design effort underestimated
- Testing treated as optional
- No buffer for changes or unknowns
- Ignoring post-launch support costs
A professional project cost calculation explicitly accounts for these realities instead of hoping they won't happen.
Core Components of Project Cost Calculation
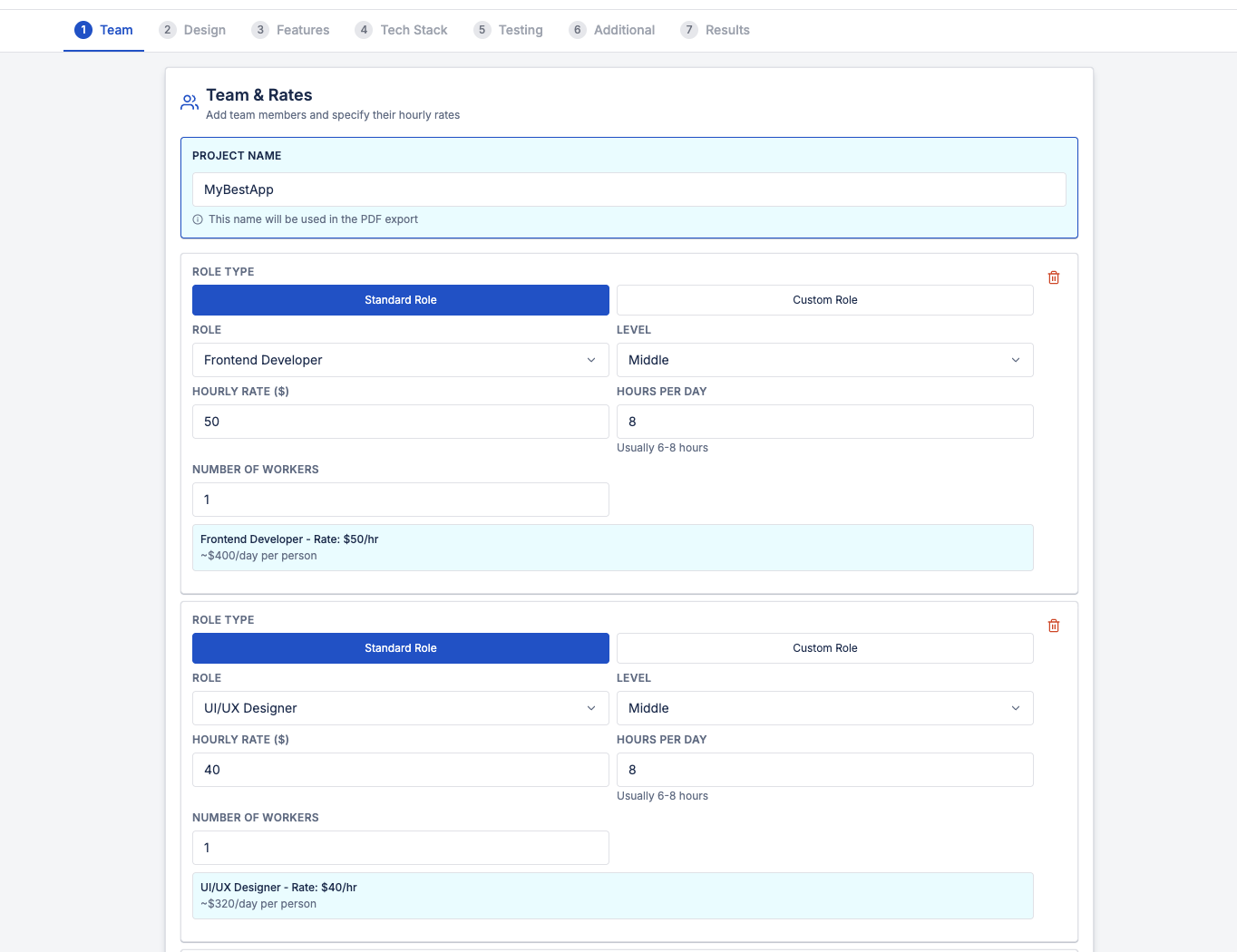
1. Team Composition and Rates
Every software project is built by people — and people are the primary cost driver.
A realistic estimate starts with defining:
- Roles (frontend, backend, QA, design, management)
- Skill level (junior, middle, senior)
- Hourly rates
- Number of team members
- Daily availability
For example, a single frontend developer working 8 hours per day at $50/hour already represents $400 per day, before adding any other roles.
Ignoring team structure is one of the fastest ways to miscalculate project cost.
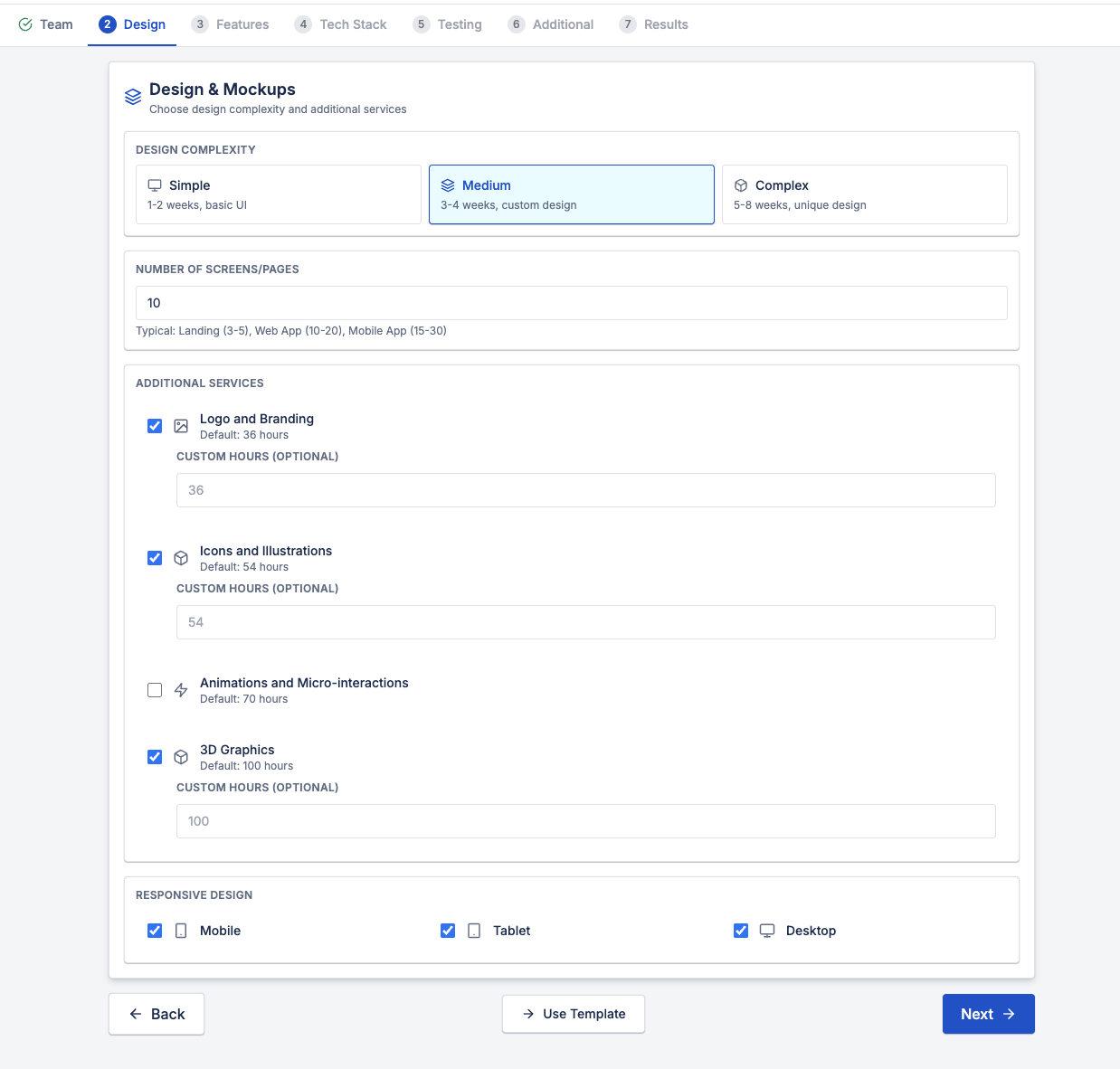
2. Design Complexity and Scope
Design is not just "making screens look nice." It includes:
- User flows
- Interaction logic
- Responsive layouts
- Platform-specific variations
Project cost calculation should consider:
- Design complexity (simple, medium, complex)
- Number of screens or pages
- Additional services such as branding, illustrations, animations, or 3D assets
- Target platforms (mobile, tablet, desktop)
A web app with 10 screens and medium complexity can require weeks of design effort, not days.
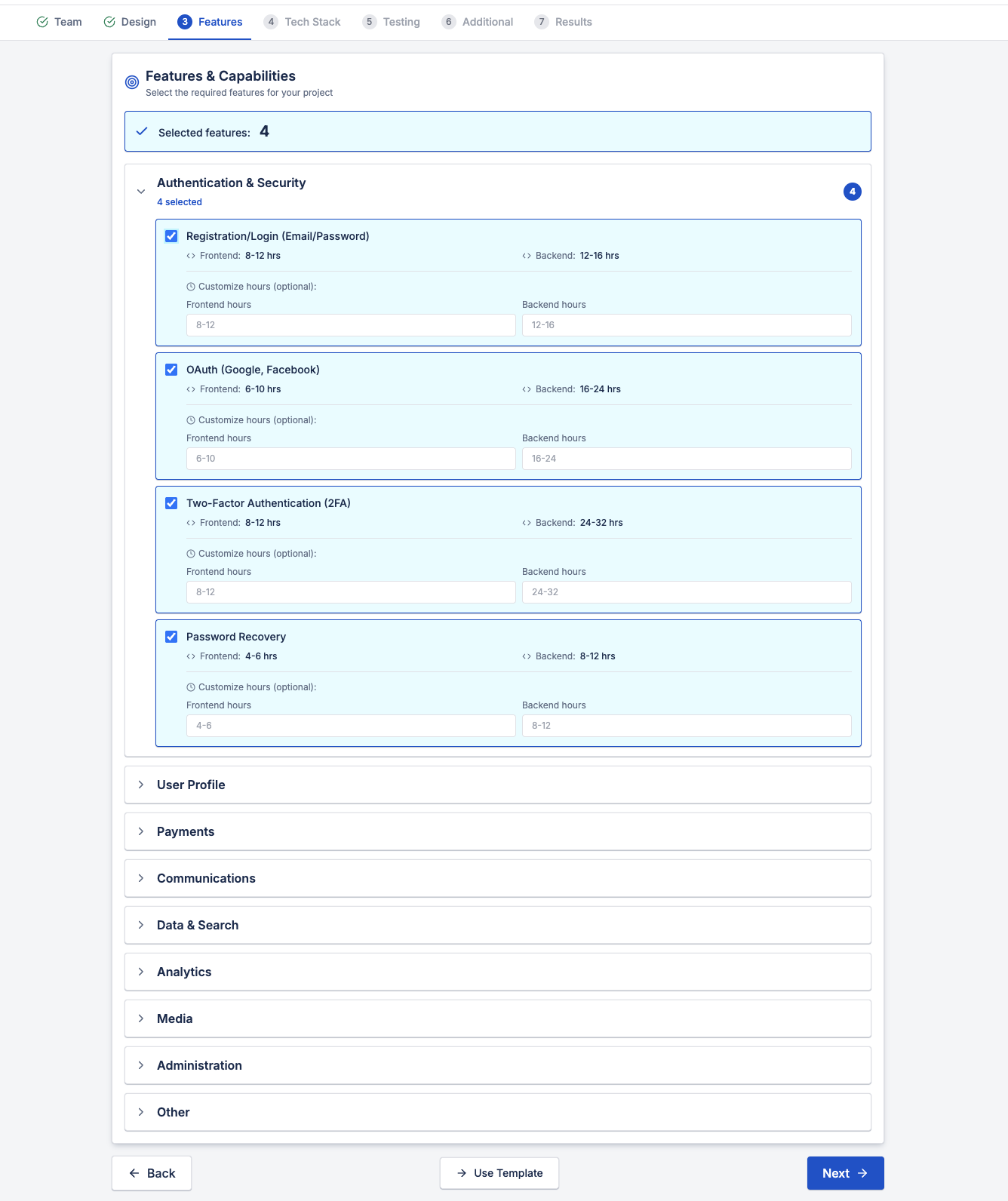
3. Features and Functional Capabilities
Features are where most project budgets grow — and where estimation mistakes are most costly.
A professional calculation breaks features into categories such as:
- Authentication and security
- User profiles
- Payments and subscriptions
- Communication features (chat, notifications, video)
- Data handling and search
- Analytics and reporting
- Administration and moderation
- Media processing
- Integrations with third-party services
Each feature has frontend and backend effort, and often hidden complexity in testing and edge cases.
Counting features without estimating effort is not estimation, it's guessing.
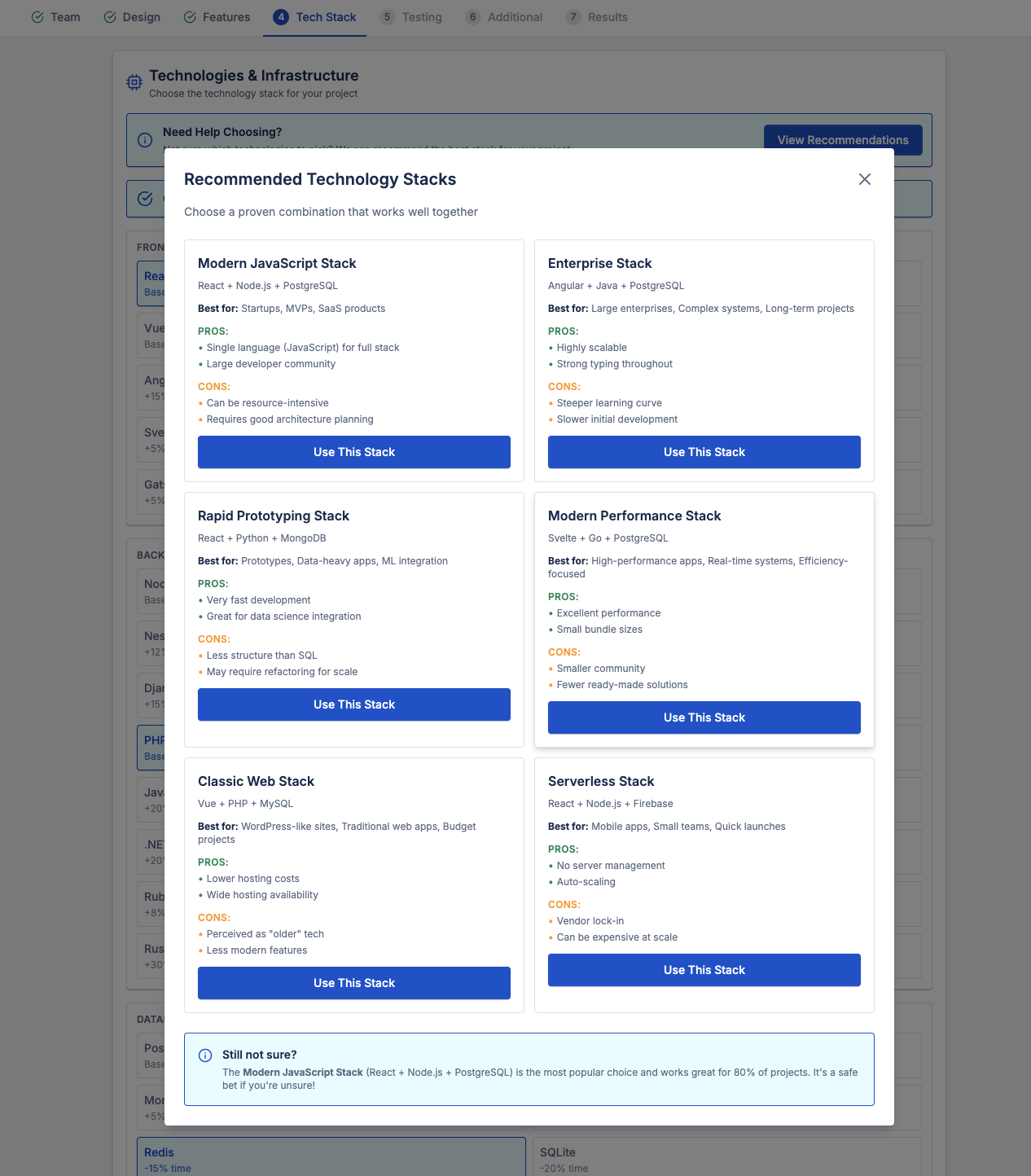
4. Technology Stack and Architecture
Technology choices affect:
- Development speed
- Maintenance cost
- Scalability
- Security requirements
Different stacks introduce different complexity levels. For example:
- Real-time features require additional backend infrastructure
- Payment systems require compliance and validation logic
- APIs and integrations require coordination with external services
A proper project cost calculation aligns technical decisions with business goals, not trends.
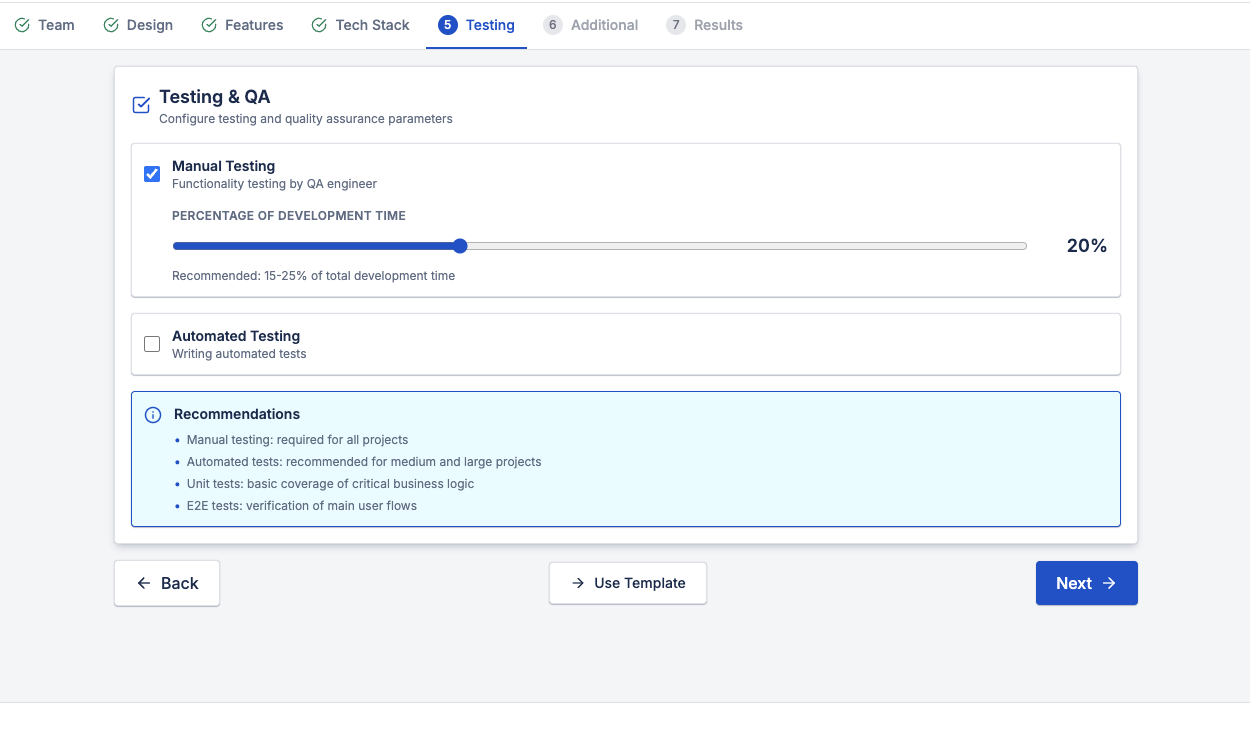
5. Testing and Quality Assurance
Testing is not optional if reliability matters.
Project cost calculation should include:
- Manual testing as a percentage of development time
- Automated tests for medium and large projects
- Coverage of critical business logic
- End-to-end user flow verification
Industry benchmarks typically allocate 15–25% of development time to QA. Projects that skip this phase often pay much more later.
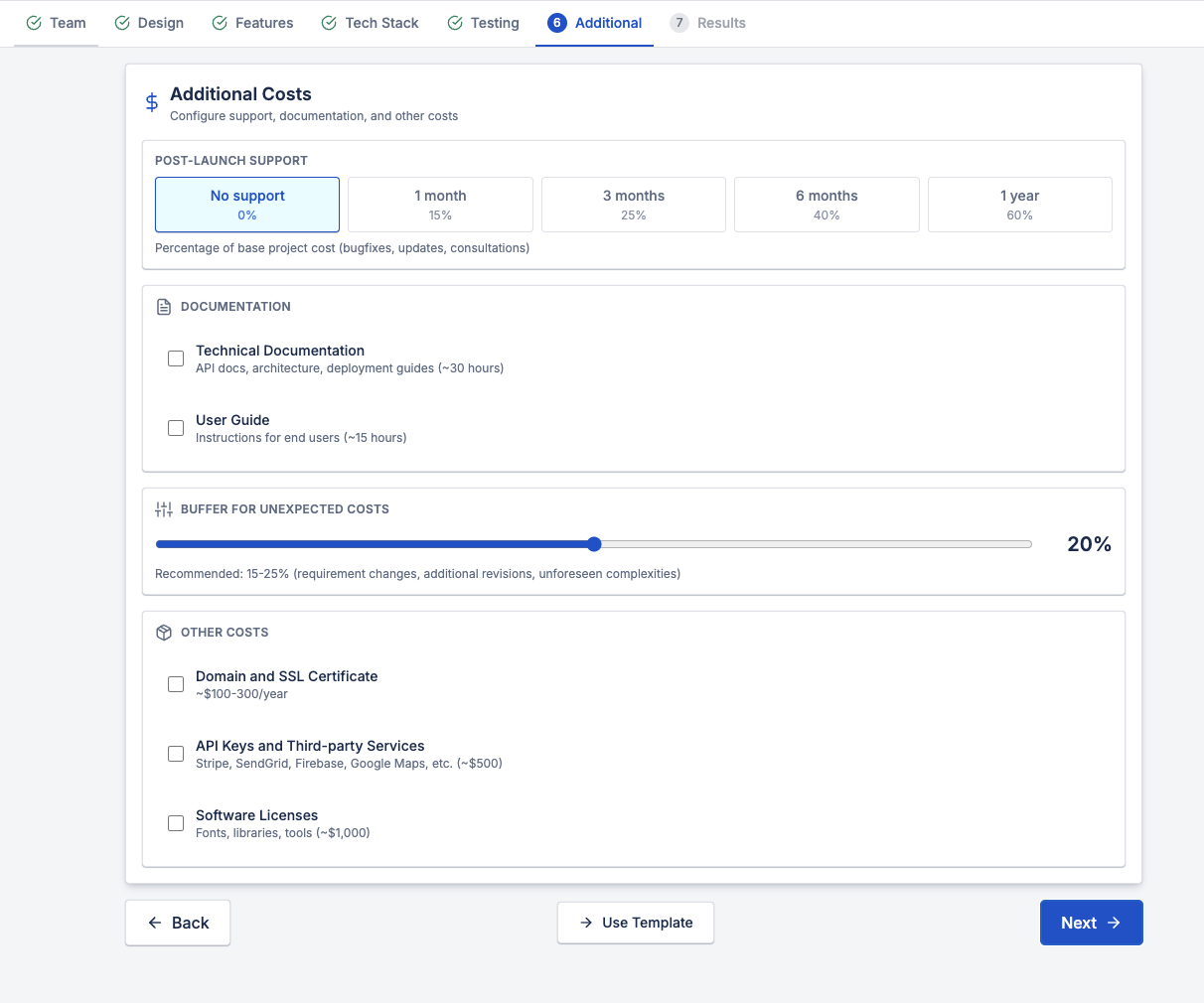
6. Additional and Hidden Costs
Many estimates fail because they stop at "development complete."
Real projects often include:
- Post-launch support and maintenance
- Technical documentation
- User guides
- Buffer for requirement changes
- Domain, SSL, and third-party service costs
- Software licenses and tooling
A buffer of 15–25% is not pessimism — it's realism.
Fixed Price vs Time & Materials
Understanding pricing models is essential for accurate cost calculation.
Fixed price works best when:
- Scope is fully defined
- Requirements are unlikely to change
- Risk is transferred to the vendor (at a premium)
Time & materials is better when:
- Scope evolves
- Flexibility is required
- Transparency matters
Most modern software projects are better served by estimation ranges, not fixed promises.
Why Single-Number Estimates Fail
Software development is not manufacturing. Unknowns are inevitable.
Single-number estimates:
- Ignore risk
- Create false confidence
- Break trust when reality differs
Professional project cost calculation uses ranges to reflect uncertainty while still enabling planning.
How Modern Tools Improve Project Cost Calculation
Modern estimation tools structure the process by:
- Breaking projects into roles, features, and stages
- Applying realistic effort ranges
- Converting effort into cost using real rates
- Making assumptions visible and adjustable
This approach mirrors how experienced agencies and product teams plan projects internally.
How Projekto Calculates Project Cost
Projekto follows industry-standard estimation principles:
- Role-based effort modeling: Each role contributes time based on selected features and scope.
- Design and feature complexity scoring: Effort scales with screens, interactions, and technical depth.
- Parallel work consideration: Timelines reflect multiple roles working simultaneously.
- Testing and QA allocation: Quality assurance is included, not optional.
- Additional costs and buffers: Real-world overhead is built into the final estimate.
Results are presented as transparent ranges, not artificial certainty.
When Should Estimates Be Refined?
Project cost calculation is iterative.
You should refine estimates when:
- Requirements become clearer
- Technical decisions are finalized
- External dependencies are confirmed
- Scope changes significantly
Early estimates guide decisions. Later estimates guide execution.
Start Your Project Cost Calculation
Accurate project cost calculation doesn't require weeks of spreadsheets or guesswork.
Using a structured estimation approach allows you to:
- Understand cost drivers
- Compare options
- Plan realistically
- Reduce risk before committing budget
FAQ
What is project cost calculation?
Project cost calculation is the process of estimating the total budget required to design, develop, test, and deliver a software project. It includes team costs, design effort, feature complexity, testing, and buffers for unexpected changes.
Why is project cost calculation difficult for software projects?
Software projects involve changing requirements, technical uncertainty, and multiple roles working in parallel. These factors make single-number or fixed estimates unreliable without structured cost modeling.
What factors affect project cost calculation the most?
The biggest cost drivers are team composition and hourly rates, design complexity, number and complexity of features, technology stack decisions, testing requirements, and buffers for unforeseen work.
Does project cost calculation include testing and QA?
Yes. A realistic project cost calculation includes both manual and automated testing. Industry best practices typically allocate 15–25% of total development time to quality assurance.
Should project cost estimates be a fixed number?
No. Professional project cost calculation uses ranges rather than fixed numbers to reflect uncertainty, scope changes, and differences in execution between teams.
When should project cost estimates be updated?
Estimates should be refined as requirements become clearer, technical decisions are finalized, and scope changes occur during planning or execution.
Can project cost calculation be done at the idea stage?
Yes. High-level project cost calculation can be performed early using assumptions about scope, features, and team structure. Accuracy improves as more details are defined.